What is melasma and what are possible treatments
SANTÉ - Si vous avez des taches foncées sur le visage qui ne disparaissent pas, vous pourriez être touché par un type d’hyperpigmentation appelé mélasma.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, the melasma affects nearly five million Americans, mainly women.In France, little data is available on the subject.This condition could be more common in pregnant women and those taking oral contraceptives according to the International Skin Institute and Doctor Claudia Aguirre quoted by the Eucerin brand.According to a 2008 study by the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Marrakech, out of a group of 60 pregnant women, only 5% have developed a chloasma or pregnancy mask.
This condition caused by a hormonal change and sun exposure has no health risk.The melasma can fade with adequate care, even if you will not necessarily find a perfectly unified complexion.On the other hand, ill -treatment can worsen the situation and certain lightening products found on the market can be dangerous.
The HuffPost asked a few dermatologists to identify safe treatments and limit the appearance of melasma, especially in this period when you are most exposed to the sun.
What is melasma?
The melasma is in the form of brown spots with irregular shapes that appear on the skin when melanocytes (pigment cells of the skin) produce too much melanin.The mechanism is different from "other forms of hyperpigmentation, as in the spots left by scars and acne," explains Jeremy Fenton, certified dermatologist.
Most often, the melasma appears on the forehead, the upper lip and the cheeks.Women are more affected than men, and people with matte skin are particularly exposed, without anyone knowing why.
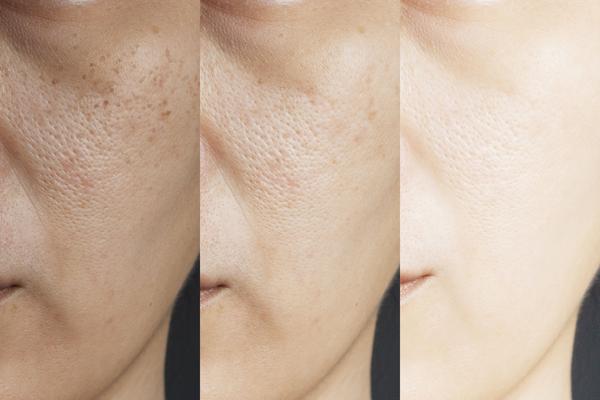
The "melasma can be episodic and worsens during the increase in estrogen levels, especially during pregnancy," said Marisa Garsish, certified dermatologist.
The spots can darken notably by exposing itself to the sun and it is sometimes enough to spend a few minutes in front of a window to trigger it."The melasma is extremely sensitive to light," adds Jeremy Fenton.
It seems that the blue light aggravates it, adds Marisa Garsishk.It is therefore recommended to use a sunscreen "SPF 30 or more with a wide spectrum which protects against blue light".
It is essential to limit exposure to the sun
Favor solar creams containing zinc or titanium, which form a physical barrier against UVA and UVB and limit your exposure to rays.Against blue light, Marisa Garshich recommends a formula with iron oxide.
Large -edged hats cover the face better than a cap and are therefore a better option according to Brendan Camp, certified dermatologist.He also suggests those who suffer from melasma to wear other protective clothes, such as a multi-use bandana that can put themselves around the neck or on the head.
He adds that "several brands currently offer masks with SPF for the face" which can reduce exposure to the sun if they are associated with sunscreen.
Of course, sunscreen must be put regularly throughout the day.
Try this safe care
By treating the melasma with a topical product, we “prevent melanocytes from producing pigments,” explains Jeremy Fenton.In other words, we try to clarify the stains of melasma.
Two types of lightening products are available over the counter: formulas with or without hydroquinone.
Products containing 2% hydroquinone, used for many years, are considered the most effective treatment against melasma.Dermatologists can also prescribe products with a concentration of 4%, but do not believe that the more there are, the better.Prolonged use or too high doses of hydroquinone can cause paradoxical hyperpigmentation called exogenous ochronosis, warns Marisa Garsihck.
Even if you are content with 2% over-the-counter hydroquinone products, do not hesitate to also consult a dermatologist and above all, weigh down patience: the first results can only appear after three months.
Lightening products without hydroquinone owe their effectiveness to Azélaic or Kojic acids, which eliminate pigment cells by chemical exfoliation.This type of product should be used with topical antioxidants to soothe inflammation.Marisa Garsish and Brendan Camp have a predilection for products with vitamin C which repairs the damage caused by free radicals, unifies the complexion and lightening it, which is one more advantage.
Do not force exfoliation."Aggressive exfoliating treatment can give the impression of a short -term improvement, but there is often a rebound effect," warns Jeremy Fenton."This is one of the biggest errors made by patients."
In the event of a refractory melasma, dermatologists can offer a chemical peel made in the office, or prescribe products that combine hydroquinone, retinoid and steroid.
Treatments to avoid
Many products sold online to treat hyperpigmentation is ineffective and potentially dangerous.An article in the Harvard Health warns against lightening products based on oral or injection glutathione, as they can affect renal functions and those of the thyroid.
You must also be wary of the so-called lightening home remedies, warns Brendan Camp."Lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, onions and garlic can make the skin even more sensitive to the sun or cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation," he concludes.
This article, published on the American HuffPost was translated by Valeriya Macogon for Fast Forword.
To see also on the HuffPost: EnjoyPhoenix is revealed without makeup to talk about his hormonal acne
Jill di Donato
Writer, Author of 'Beautiful Garbage: a novel'
Codeco of December 3, 2021: the new measures target schools, masks, events, but not the horeca
GO
Sunburn: how to make up for the damage? - Miss
GO
How to Get Free N95 Masks from the US Government
GO
Beauty coaching: can I apply oil if I have oily skin?
GO